www.aljazeerah.info
News, November 2014
Archives
Mission & Name
Conflict Terminology
Editorials
Gaza Holocaust
Gulf War
Isdood
Islam
News
News Photos
Opinion Editorials
US Foreign Policy (Dr. El-Najjar's Articles)
www.aljazeerah.info
|
Editorial Note: The following news reports are summaries from original sources. They may also include corrections of Arabic names and political terminology. Comments are in parentheses. |
China's Unmanned Lunar Orbiter, Xiaofei, Returns Home Successfully After 8-Day Mission
November 1, 2014
 |
|
|
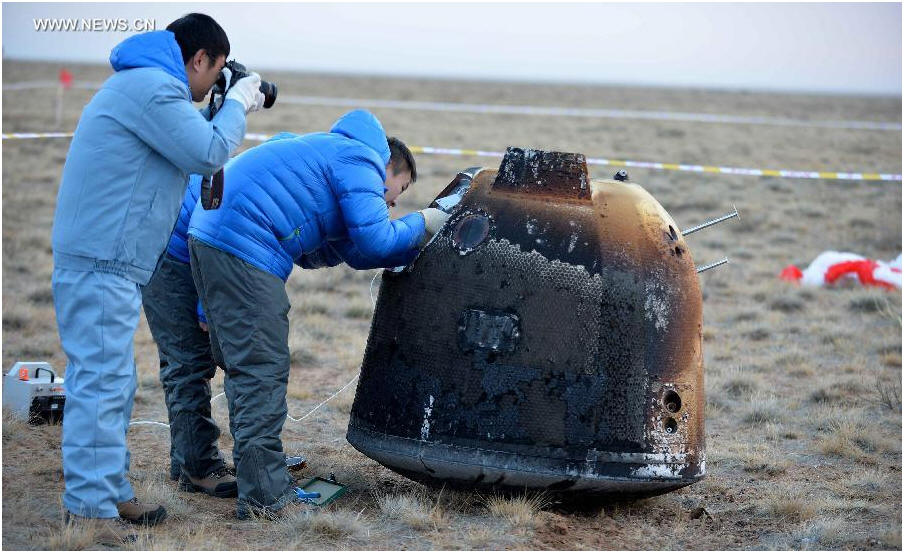
Researchers retrieve the return capsule of China's unmanned lunar orbiter in the central region of north China's Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, November 1, 2014 (Xinhua/Ren Junchuan) |
Right click on photos for information about them
China's unmanned lunar orbiter returns home, first in nearly four decades
BEIJING, Nov. 1, 2014 (Xinhua) --
China succeeded Saturday in the world's first mission to the Moon and back in some 40 years, becoming the third nation to do so after the former Soviet Union and the United States.
The test lunar orbiter, nicknamed "Xiaofei" on Chinese social networks, landed in Siziwang Banner of China's Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region early Saturday morning.
Search teams have already recovered the orbiter at the designated landing area, about 500 kilometers away from Beijing.
The last documented mission of this kind was by the Soviet Union in the 1970s.
Launched Friday last week, the orbiter traversed 840,000 kilometers on its eight-day mission that saw it round the far side of the Moon and take some incredible pictures of Earth and Moon together.
The re-entry process began at around 6:13 a.m. Saturday morning, with the orbiter approaching Earth at a velocity of about 11.2 kilometers per second.
The high speed led to hefty friction between the orbiter and air and high temperatures on the craft's exterior, generating an ion sheath that cut off contact between ground command and the orbiter.
To help it slow down, the craft is designed to "bounce" off the edge of the atmosphere, before re-entering again. The process has been compared to a stone skipping across water, and can shorten the "braking distance" for the orbiter, according to Zhou Jianliang, chief engineer with the Beijing Aerospace Command and Control Center.
"Really, this is like braking a car," said Zhou, "The faster you drive, the longer the distance you need to bring the car to a complete stop."
The "bounce" was one of the biggest challenges of the mission, because the craft must enter the atmosphere at a very precise angle. An error of 0.2 degrees would have rendered the mission a failure.
Wu Yanhua, vice director of China's State Administration of Science, Technology and Industry for National Defense, said the successful test mission has gathered a lot of experimental data and laid a solid foundation for future missions.`
PAVING WAY FOR NEW PROBE
The eight-day program is a test run for the final chapter of China's three-step--orbiting, landing and finally returning--lunar program.
"Xiaofei" is obtaining data and validating re-entry technology such as the heat shield and trajectory design for a future landing on the moon by Chang'e-5.
Earlier reports said Chang'e-5 will be launched around 2017. The goal is to collect samples from the Moon and return to Earth. If successful, China will become the third nation to do so.
Calling "Xiaofei" a pathfinder for Chang'e-5, Zhou Jianliang said the data acquired by the lunar orbiter will optimize technology for Chang'e-5.
Hao Xifan, deputy chief of China's third phase lunar exploration program, also said the mission validated ground support capacities, craft landing technology and recoverable spacecraft technology.
According to Wu Weiren, chief designer of China's lunar exploration program, Chang'e-5 is expected to collect a 2-kg sample from two meters under the Moon's surface and bring it home.
Aside from the high-speed re-entry, major technological challenges for the craft center on surface sampling, taking off from the Moon, and lunar orbit rendezvous, Wu said.
READY TO MAKE HISTORY, AGAIN
China launched a pair of orbiting lunar probes and last year landed a craft on the moon with a rover on board.
Saturday's success is another step forward for China's ambition that could eventually land a Chinese citizen there. Few countries can rival China's space program although China never intended to participate in any "space race".
In an earlier interview with Xinhua, Wu Weiren said lunar probe technology and software could be of great economic value if adapted for commercial use.
Commercial gains aside, the space program is already a marker of China's global stature and technical expertise. The Chang'e lunar probes - named after a goddess who took her pet Yutu, or jade rabbit, to the moon - are a symbol of great national pride.
The country sent its first astronaut into space in 2003, becoming the third nation after Russia and the U.S. to achieve manned space travel independently. In 2008, astronauts aboard the Shenzhou-7 made China's first space walk. There are plans for a permanent space station, expected to be set up around 2022.
The Chang'e-1 and Chang'e-2 missions in 2007 and 2010 respectively, capped the orbital phase of the three step project. Chang'e-1 crashed onto the Moon's surface at the end of its mission, and Chang'e-2 was sent into deep space to become China's first man-made asteroid.
The ongoing second phase saw Chang'e-3 soft land on the moon carrying moon rover Yutu in December 2013. Chang'e-4 was a backup for Chang'e-3 and has not been deployed.
In the meantime, Yutu has entered its 11th dormancy earlier October, although its functions have degraded considerably after it encountered control issues in January this year. Experts had feared that it might never function again, but Yutu has stubbornly managed to wake up from its sleep mode ever since.
None of those missions were intended to return to Earth and this has pushed the 2017 mission further into spotlight.
"The Chang'e-5 mission will be yet another historic moment for China's lunar program," Wu said.
Space launch to pave the way for lunar expedition
BEIJING, Oct. 23, 2014 (Xinhuanet) --
China will launch an experimental spacecraft between Friday and Sunday to test a key technology designed to help a future lunar probe return to Earth with soil samples.
The unnamed spacecraft is due to reach a location near the moon before returning to Earth, said a spokesman for the China National Space Administration, which announced the launch on Wednesday.
It will be China's first lunar module to return to Earth, at a speed close to 11.2 km per second, space experts said.
Hu Hao, chief designer of the lunar exploration program's third phase, said in an earlier interview with China Daily that the re-entry speed could cause the return capsule to overheat or become difficult to track and control.
No simulated tests on Earth can recreate the challenge, he said.
The space agency spokesman said the re-entry will involve one or more "skips" off the Earth's atmosphere to slow the spacecraft before final re-entry. It is due to land in a central area of the Inner Mongolia autonomous region.
Experts said "skip re-entry" could help to disperse the huge amount of heat that is usually generated on faster descents.
Data from the United States' National Aeronautics and Space Administration show that "skip re-entry" technology was used on lunar missions by the former Soviet Union.
If successful, the technology will help the Chang'e-5 lunar probe to return to Earth with lunar soil samples around 2017, the spokesman said.
On Wednesday, technicians at the Xichang Satellite Launch Center in Sichuan province began fueling the Long March 3C rocket that will carry the experimental spacecraft.
Rocket expert Jiang Jie said that compared with the previous three launch missions this one poses the sternest test.
"The mission requires that the rocket sends the spacecraft to a fixed spot in space. Any inaccuracy will mean that the spacecraft will fail to enter the moon's orbit," she told China Central Television.
Liu Jianzhong, deputy chief engineer for the Long March 3 series rockets, said the mission will have a launch window of 35 minutes each day between Friday and Sunday.
The national space agency said the experimental mission marks the start of the third phase of China's lunar program featuring probes returning to Earth.
The country launched the Chang'e-1 probe in 2007, Chang'e-2 in 2010 and Chang'e-3 in 2013, completing experiments in orbiting and landing on the moon.
China has one moon rover, the Jade Rabbit, on the lunar surface. This craft, launched as part of the Chang'e-3 mission late last year, has been declared a success by Chinese authorities, although it has been plagued by mechanical troubles.
(Source: China Daily)
Editor: Lu Hui
***
Share this article with your facebook friendsFair Use Notice
This site contains copyrighted material the
use of which has not always been specifically authorized by the copyright
owner. We are making such material available in our efforts to advance
understanding of environmental, political, human rights, economic,
democracy, scientific, and social justice issues, etc. We believe this
constitutes a 'fair use' of any such copyrighted material as provided for
in section 107 of the US Copyright Law. In accordance with Title 17 U.S.C.
Section 107, the material on this site is
distributed without profit to those
who have expressed a prior interest in receiving the included information
for research and educational purposes. For more information go to: http://www.law.cornell.edu/uscode/17/107.shtml.
If you wish to use copyrighted material from this site for purposes of
your own that go beyond 'fair use', you must obtain permission from the
copyright owner.
|
|
|
|
||
|
||||||